Incineration Plants
The various processing and production processes of the large-scale chemical industry, food industry, petrochemical industry and the pharmaceutical industry generate gaseous or liquid wastes whose disposal requires thermal treatment and purification of the smoke and process gases.
For these applications, RVT Process Equipment supplies turnkey plants including steel construction, piping and specific EMSR, process control and safety technology. Our burner systems are designed individually for each application in order to comply with the legal framework for proper and clean disposal. When feeding the waste to be recycled, different safety regulations must be followed, depending on the medium. Generally, the media are separated via separate, specially designed exhaust or liquid lances fed to the combustion chamber. Only at the burner outlet, the residues mix with the combustion air and are completely burned.
Liquid residues are introduced into the combustion chamber either by pure pressure atomization or by atomization with auxiliary media such as air, steam or nitrogen. Depending on the medium and conditions, the technically and economically optimal solution is developed here.
If high-calorific or flammable exhaust gases are to be disposed of, a safety assessment is carried out in accordance with the ATEX Directive. If required, the exhaust pipes are equipped with static or dynamic flame arresters.
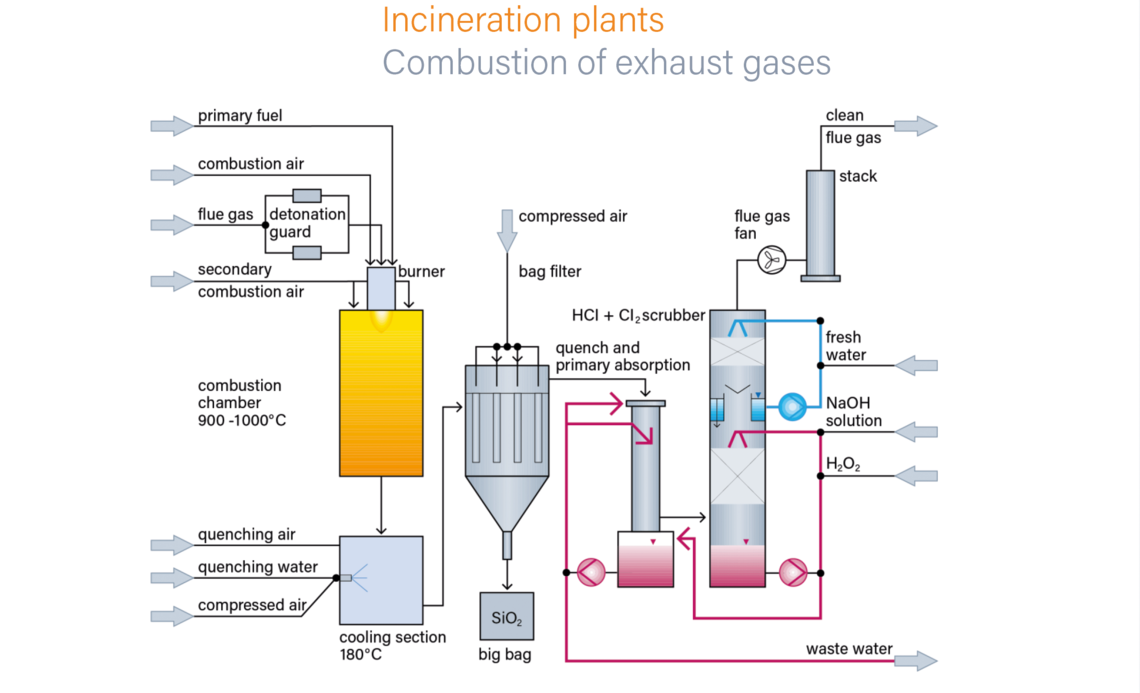
During the production of silanes and silicones as well as in the solar and semiconductor industry, silicon - and partly chlorine-containing exhaust gases are produced. Often incineration is the only way to dispose of these exhaust gases in an environmentally friendly manner.
As a special competence, RVT has been offering complete solutions in the field of silane combustion for over 10 years.
Silicon (e.g. from chlorosilanes) is converted in the flame into extremely light white silicon dioxide (SiO2) fine dust and the chlorine into HCl and Cl2 according to the Deacon equilibrium. Since the SiO2 fine dust tends to stick and sinter when the temperature is too high, a narrow temperature window must be maintained in the combustion chamber.
By arranging the combustion chamber as vertical as possible with subsequent air or water quenching, large deposits of SiO2 dust are avoided. After the fine dust has been separated in a filter system, an HCl / CL2 cleaning stage may follow.
The fact that each system is individually adapted to the respective requirements, no investment of the other. In addition to various washing stages, we also integrate a waste heat utilization by a steam boiler or a preheating of the combustion air. In addition, so-called DeNOX plants belong to our portfolio, in which ammonia is used to reduce harmful nitrogen oxides (NOX).